National Anthem At The Veterans Day
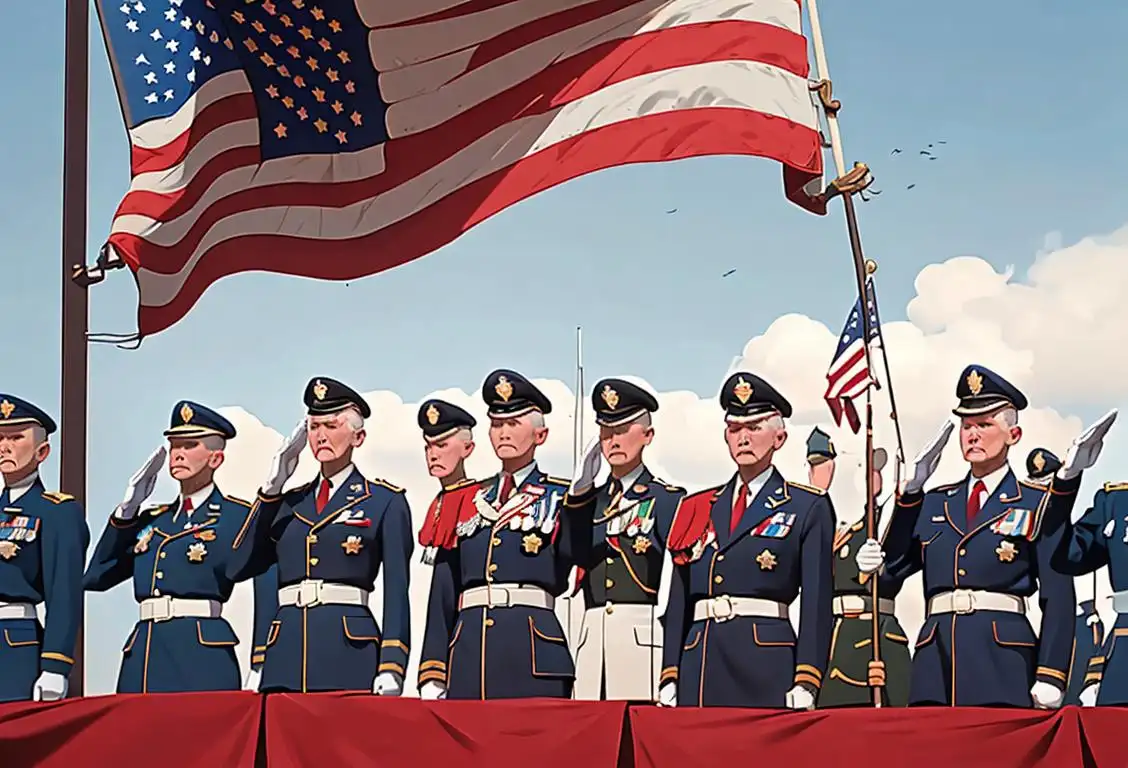

Welcome to the wonderful world of national days! Today, we're diving into the fascinating history and significance of the national anthem at Veterans Day. Get ready to learn, have some fun, and perhaps even hum a patriotic tune along the way!
When is Anthem At The Veterans Day?
It's national anthem at the veterans day on the 11th November.
The National Anthem at Veterans Day: A Resounding Tribute
When it comes to honoring our brave veterans, few things tug at the heartstrings quite like the sounds of our national anthem resonating through the air. This powerful melody serves as a symbol of our gratitude, reminding us of the sacrifices made by those who have served our country in times of war and peace.
At Veterans Day celebrations across the nation, the national anthem takes center stage, inviting us all to unite in a moment of reflection and appreciation. Whether it's sung by a soloist, a choir, or echoed by the passionate voices of a stadium crowd, the national anthem serves as a poignant reminder of the dedication and courage displayed by our veterans.
While the tradition of singing the national anthem at Veterans Day events is deeply rooted in patriotism, it's interesting to note that the anthem itself has a rich history of its own.
Did You Know?
Did you know that the national anthem of the United States, 'The Star-Spangled Banner,' was inspired by a battle during the War of 1812? It was written by Francis Scott Key after witnessing the British bombardment of Fort McHenry in Baltimore Harbor. Talk about finding inspiration in the face of danger!
History behind the term 'Anthem At The Veterans'
1814
The Star-Spangled Banner
In September 1814, during the War of 1812 between the United States and Great Britain, a young American lawyer named Francis Scott Key witnessed the bombardment of Fort McHenry in Baltimore. Inspired by the sight of the American flag still waving after the 25-hour attack, Key penned a poem called 'Defence of Fort M'Henry'. The poem was later set to the tune of a British drinking song called 'To Anacreon in Heaven'. This musical adaptation became known as 'The Star-Spangled Banner'.
1889
Adoption as National Anthem
The popularity of 'The Star-Spangled Banner' as a patriotic song grew steadily over the years. In 1889, the secretary of the Navy, Benjamin F. Tracy, ordered that it be played for the raising of the flag at military occasions. This increased exposure helped solidify its status as the unofficial national anthem of the United States. However, it wasn't until March 3, 1931, that 'The Star-Spangled Banner' was officially designated as the U.S. national anthem by a congressional resolution signed into law by President Herbert Hoover.
World War II Era
Association with Veterans
During World War II, the singing of the national anthem became a prominent fixture at events honoring and supporting veterans. The anthem was performed at military funerals, memorial services, and parades, evoking patriotism and honoring the sacrifices made by servicemen and women. It became a powerful symbol of unity and resilience in times of war, serving as a reminder of the nation's values and the strength of its armed forces.
1980
Introduction of National Veterans Day Ceremony
In 1980, the United States Department of Veterans Affairs organized the first official National Veterans Day Ceremony held at the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in Arlington National Cemetery. This annual ceremony marked a significant moment for veterans, and the national anthem took on even greater significance during the event. It became customary for the anthem to be performed as part of the solemn tribute to honor the nation's veterans and their service.
Did you know?
Did you know that the national anthem of the United States, 'The Star-Spangled Banner,' was inspired by a battle during the War of 1812?Tagged
awareness fun rememberanceFirst identified
8th November 2016Most mentioned on
11th November 2016Total mentions
75Other days
Voters Day
Unemployed Day
Suicide Prevention Day
Cancer Survivors Day
Memorial Day
Bestfriends Day
Heroes Day
Liberation Day
Pumpkin Day
Gymnastics Day